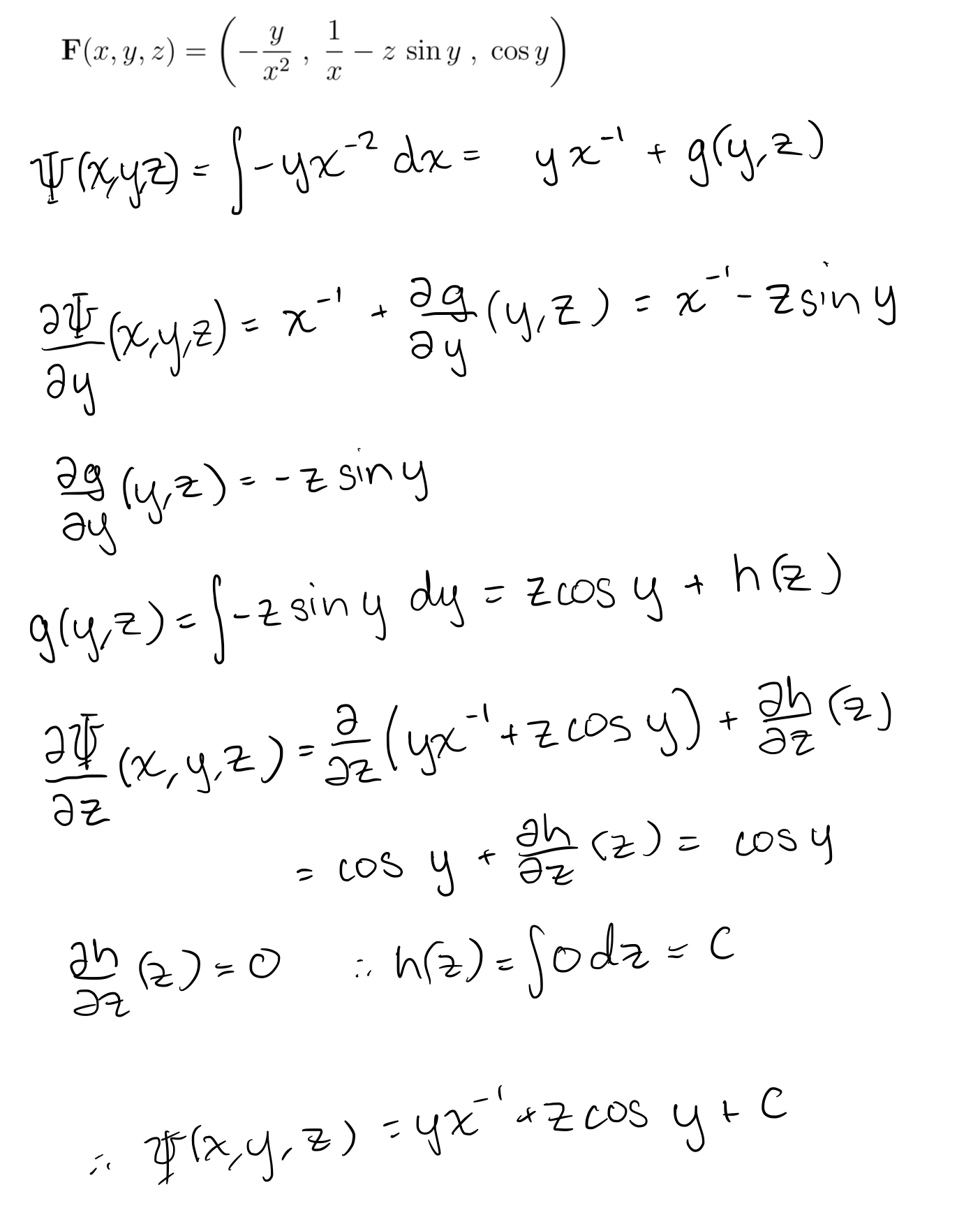Conservative vector field
A conservative vector field1 is a Vector field in which the line integral is path-independent, i.e. only depends on the start and end points. vec
Any conservative vector field may be expressed as the gradient field of some scalar field, called the scalar potential, such that
Deriving a scalar potential
Properties and examples
- The Circulation around any closed path is
- The Curl of any conservative vector field
(this follows from Stokes’s theorem). The converse is true on any Simply connected space. - Fundamental theorem for line integrals may be used
Partially conservative field
As a consequence of Stokes’s theorem,
if a simply connected region is irrotational w.r.t. a field (i.e.
Practice problems
Practice problems are mostly for deriving a potential.
- 2023. Advanced Mathematical Methods, p. 28 (§1 problems 12–15)
- 2016. Calculus, pp. 1124–1135 (§16.3 exercises 3–19)
- 2016. Calculus, pp. 1149 (§16.5 exercises 13–18)
Footnotes
-
also called irrotational ↩
-
For an example of this in the two dimensional case, see 2023. Advanced Mathematical Methods, pp. 31–32. ↩