System of linear equations
A system of linear equations is a set of linear equations considered collectively, linalg i.e. equations of the form
where a solution to the system involves determining value(s) of each
- A special type of system of linear equations is the Homogenous system of linear equations.
- It is also common to write such a system in the equivalent matrix representation.
Number of solutions
Systems of linear equations may either have zero, one (unique), or infinite solutions. Only systems with at least as many equations as unknowns can have a single solution, but such a system can also have zero or infinite solutions.
Zero solutions
Zero solution systems can typically be interpreted geometrically with some notion of parallelism.
For example, a zero solution equation in a
For a
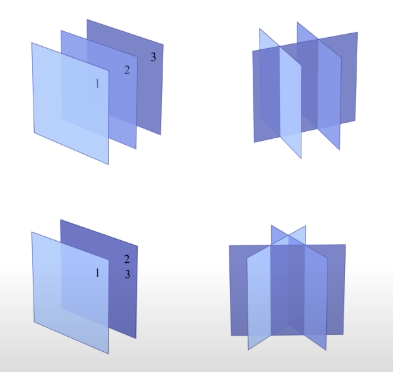
One unique solution
One solution occurs when neither of the following occur
- No lines (2 variables) or planes (3 variables) are parallel.
- No lines/planes can be made orthogonal to each respective line/plane such that these orthogonal lines/planes are all parallel.
Infinite solutions
Geometrically, infinite solutions will occur either if all three planes overlap entirely, that is to say that all three planes are one and the same; or if the three planes all intersect along a single line, radiating outwards like spokes from an axis.
Footnotes
-
Henceforth any discussion of dimension of a system corresponds to the dimension of the coefficient matrix in the system’s matrix representation. ↩