Tangent space
The tangent space
Intrinsic manifold
The following characterizations of
As derivations at a point
Let
, and suppose is the set of vector fields viewed as derivations. We define the tangent space as the image of the map i.e. the set of all derivations evaluated at
.
Chart-free characterization as velocities
Let
, be a chart at , and be the set of all [[Differentiability|
]] paths such that . We define an equivalence relation on so that two paths are equivalent iff which is easily shown to be independent of choice of
. [!missing]- From the cotangent space
The tangent space is the dual of the Cotangent space, which can be defined directly.
Via the cotangent space
The cotangent space
admits an intrinsic characterization, which is applicable in other (non-differentiable) settings. The tangent space is simply the dual vector space .
Equivalence of characterizations
Real embedded manifold
Both the following characterizations of the tangent space of a real embedded manifold is useful.
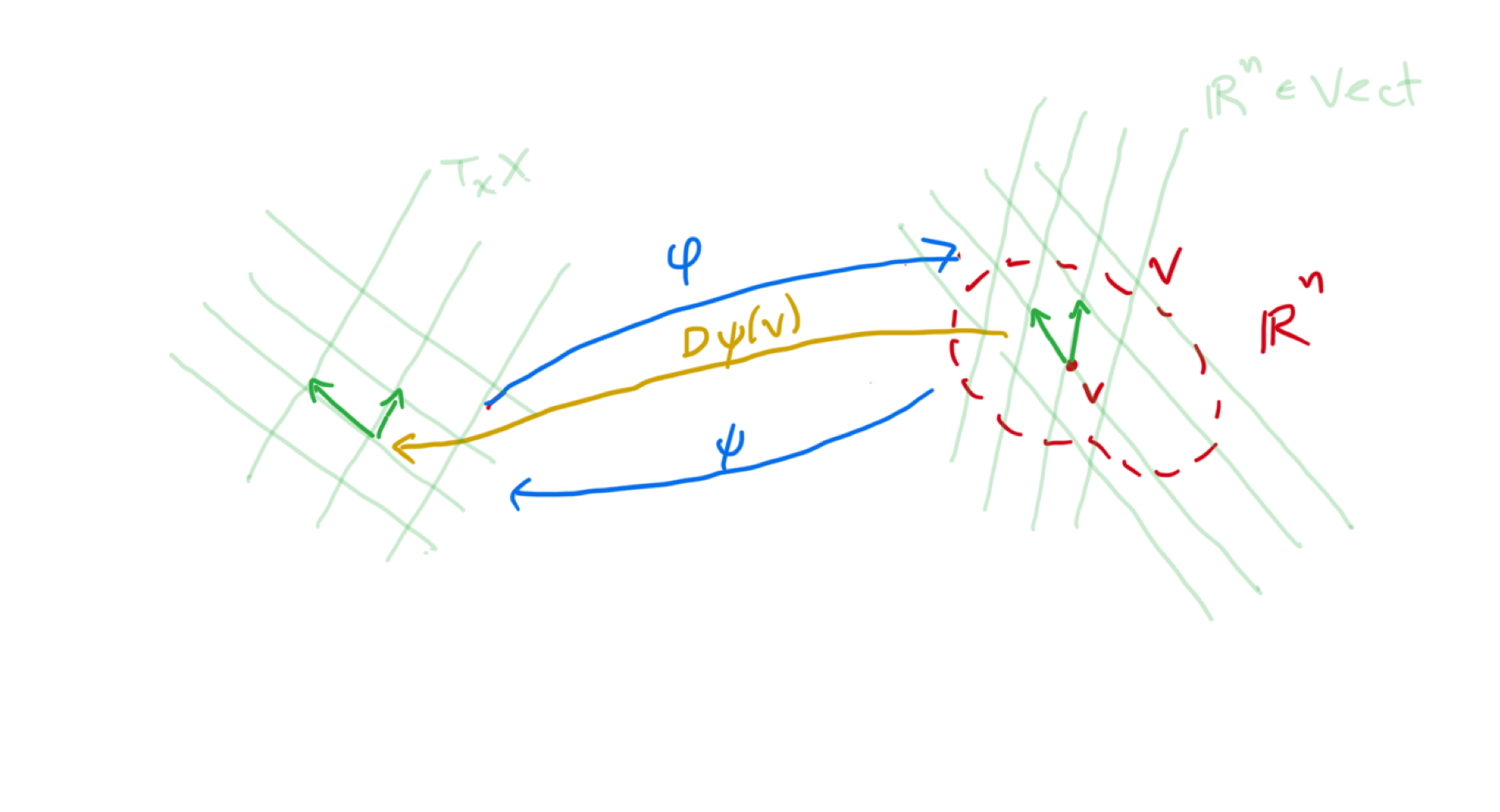
Fixed chart characterization
Let
be a Real embedded manifold and . Let be a local parameterization at
, and be its Total derivative. Then is the tangent space at .
Chart-free characterization as velocities
Let
be a Real embedded manifold and . Let be the set of all
differentiable paths such that . Then the set of all “velocities at ” is the tangent space at
.
The primary advantage of the fixed chart characterization is that its vector space status is clear, whereas the chart-free characterization is more intuitive and establishes chart-independence.
Equivalence of characterizations
Take a coördinate chart
with . Let and let denote the fixed-chart characterization and denote the chart-free characterization. Let
for some differentiable with . Then Herefore
. Now let
for some . Define and let
(we choose so that remains in ). It follows and . Herefore . Thus
.