Continuity
In its most general form, a function between topological spaces
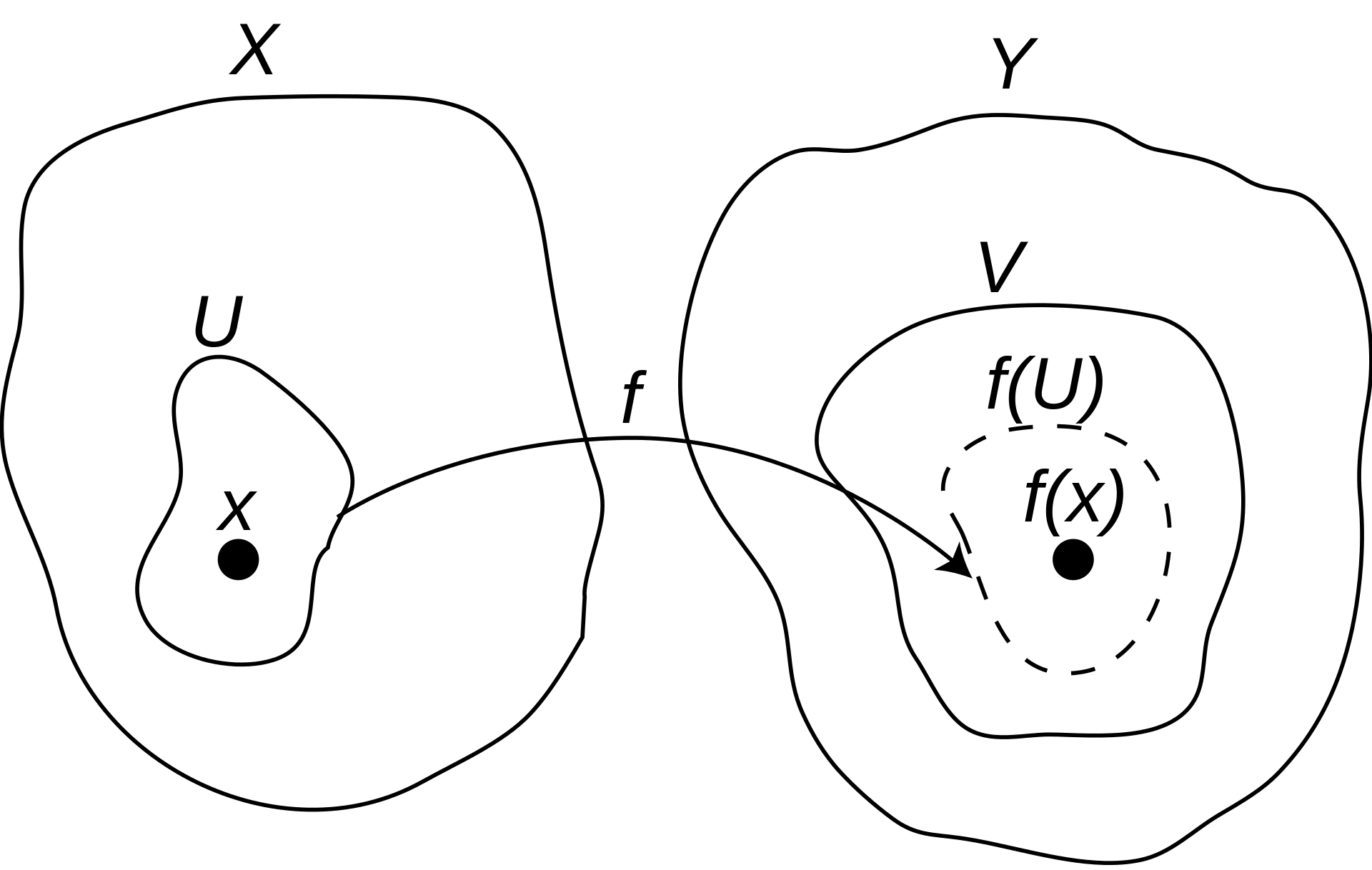
A function is continuous iff. it is continuous at every point in its domain,
or equivalently iff. the preïmage of every open set is open. topology Category of topological spaces has such functions as its morphisms.
We write
Proof of equivalence of open and general neighbourhood pointwise definitions
Let
and be topological spaces, and . First assume for every open neighbourhood
of , there exists an open neighbourhood of , such that . Given an arbitrary neighbourhood of , there exists an open neighbourhood such that . Thence there exists an open neighbourhood of , such that . Therefore for every neighbourhood of , there exists a neighbourhood of , such that . For the converse, assume for every neighbourhood
of , there exists a neighbourhood of , such that . Let be an open neighbourhood of . Then there exists a neighbourhood of such that . It follows there exists an open neighbourhood of , such that . Therefore for every open neighbourhood of , there exists an open neighbourhood of , such that .
Proof of equivalence of pointwise and preïmage definition
Let
and be topological spaces, and . First assume the preïmage of every open set is open. Let some
, and be an open neighbourhood of . The preïmage is then an open neighbourhood of , and (image of preïmage). Therefore, given any and any open neighbourhood of , there exists an open neighbourhood of such that . For the converse, assume given any
and any open neighbourhood of , there exists an open neighbourhood of such that . Let be an open set. For every , let be an open neighbourhood of such that . Take the union , which is an open neighbourhood of every , whence Since every it follows that , whence . Thus is open. Therefore the preïmage of every open set is open.
A continuous bijection with a continuous inverse is a Homeomorphism2.
Special cases
In a metric space
If
A function
is continuous at a point iff. for every there exists such that , i.e. for any .
In metric spaces continuity is equivalent to Sequential continuity,
namely a function is continuous at a point
In the real numbers
Intuitively, a function is continuous if it has no gaps,
i.e. for
and
A function which is differentiable at
Hypernyms include